Cell刊登最新文章 揭示猛犸象皮肤样本中三维基因组结构
发布时间:2024年07月15日
Sandoval-Velasco, M. et al. (2024) ‘Three-dimensional genome architecture persists in a 52,000-year-old woolly mammoth skin sample’, Cell, 187(14), pp. 3541-3562.e51. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2024.06.002.
古代DNA的分析通常涉及测序保存下来的短寡核苷酸,并将其与相关现代物种的基因组组装进行比对。本文报告了一头死于52,000年前的雌性猛犸象(Mammuthus primigenius)的皮肤样本,保留了其古代基因组结构。作者使用PaleoHi-C技术绘制染色质接触图谱并组装其基因组,得到28条染色体长度的支架。染色体区域、隔间、环、巴尔小体和失活的X染色体(Xi)超级域仍然存在。猛犸象皮肤中活跃和不活跃的基因组隔间比其他大象组织更接近亚洲象皮肤。作者的分析揭示了新的生物学知识。隔间化的差异揭示了在猛犸象和大象之间转录可能发生变化的基因。猛犸象的Xi具有四分结构,而不像人类和小鼠那样为二分结构。作者假设,在这头猛犸象死后不久,样本在西伯利亚的寒冷中自发冻干,导致玻璃化转变,从而在纳米级别保存了古代染色体的亚化石。
参考辅助的3D基因组组装方法生成了猛犸象的染色体水平基因组
作者尝试组装猛犸象的基因组。由于现有的基于Hi-C技术的哺乳动物基因组去新组装方法通常需要数亿个接触点,作者开发了一种新的基因组组装方法,称为“参考辅助3D基因组组装”,该方法使用远少于传统方法的接触点生成染色体长度支架(图2A)。该方法首先将目标物种的Hi-C数据比对到相关物种的“辅助”参考组装上。通过将Hi-C数据与辅助组装进行比较,以校正局部序列,从而生成在序列水平上与目标物种匹配的组装,但支架来自辅助组装(此步骤也可以使用aDNA-Seq)。接下来,检查接触图以识别大规模的进化变化(以及辅助组装中的错误)。作者对支架进行相应的修改,例如拆分序列并改变它们的排列和方向。这将产生一个经过修改的基因组组装,具有染色体长度的支架,即使辅助基因组组装高度碎片化,也能准确反映目标基因组。
通过将驴 (Equus asinus) 的基因组与利用马 (Equus caballus) 的基因组辅助生成的基因组组装进行比较来验证该方法。这两种生成的基因组组装结果极其相似。
然后将这一策略应用于猛犸象,利用PaleoHi-C数据与来自同一样本的aDNA测序结合,生成了一个基因组组装,名为MamPri_Loxafr3.0_assisted_HiC,辅以非洲象基因组组装Loxafr3.0。尽管Loxafr3.0存在片段化,生成的猛犸象组装包含28条染色体,涵盖3.04 Gb的序列(占总序列的97.7%),具有54 kb的contig N50长度(图2C)。整体上,获得的猛犸象和非洲及亚洲象的基因组组装在共线性方面表现出高度保守性(图S2D)。使用亚洲象组装作为辅助时,结果相似。
为了在MamPri_Loxafr3.0_assisted_HiC中注释基因,运行了TOGA。通过Benchmarking Universal Single-Copy Orthologs的完整基因检测率来评估基因注释。检测到了94.6%的完整性。
结合PaleoHi-C数据和物理建模,可以推断出猛犸象染色体的3D结构
Hi-C数据可以使用高分子物理学推断现代染色体的三维结构。为了展示这一点在古代染色体上的应用,作者构建了一组猛犸象第10号染色体的3D结构,使其与每一个单独的PaleoHi-C接触最大程度兼容,这一方法被称为直接反演(见图7A和图S8)。使用OpenMiChroM包生成的结果集合,很大程度上重现了PaleoHi-C图,并展示了哺乳动物染色体典型的球状结构。这个结果集合可以通过Spacewalk基因组浏览器进行探索。
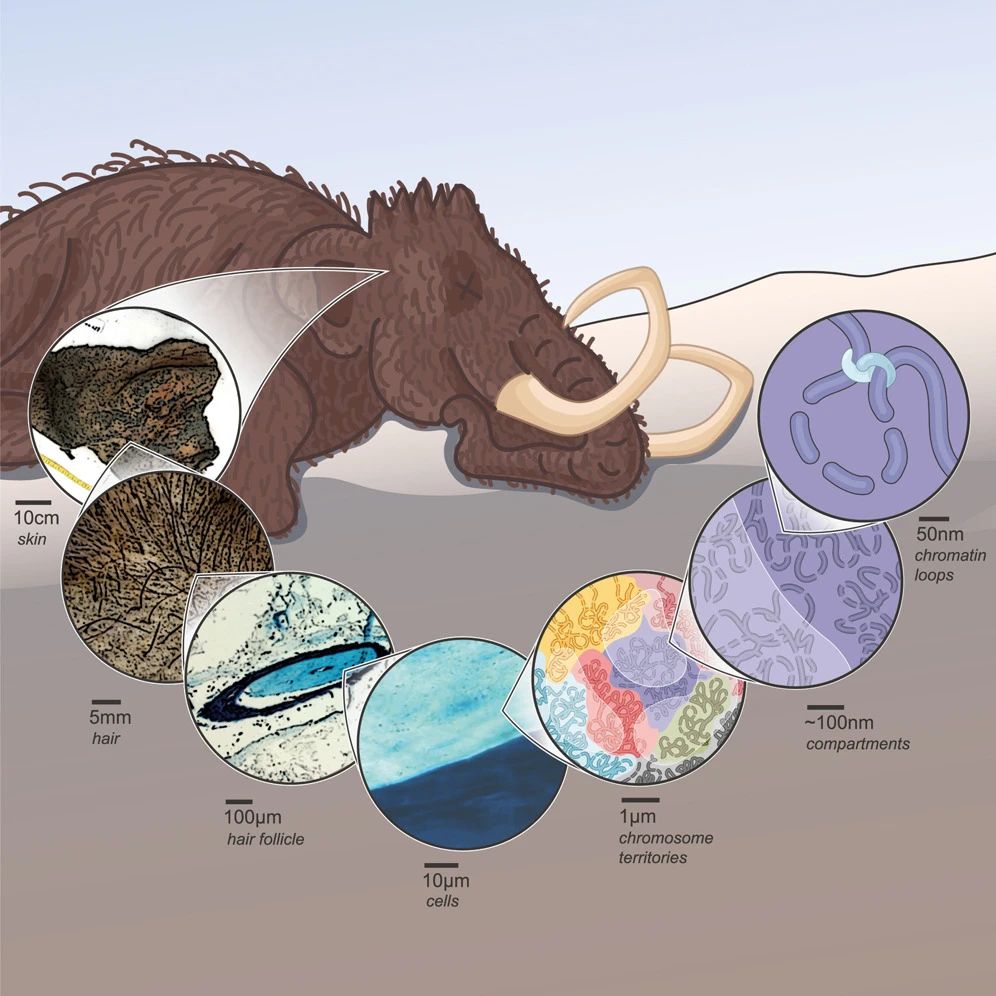
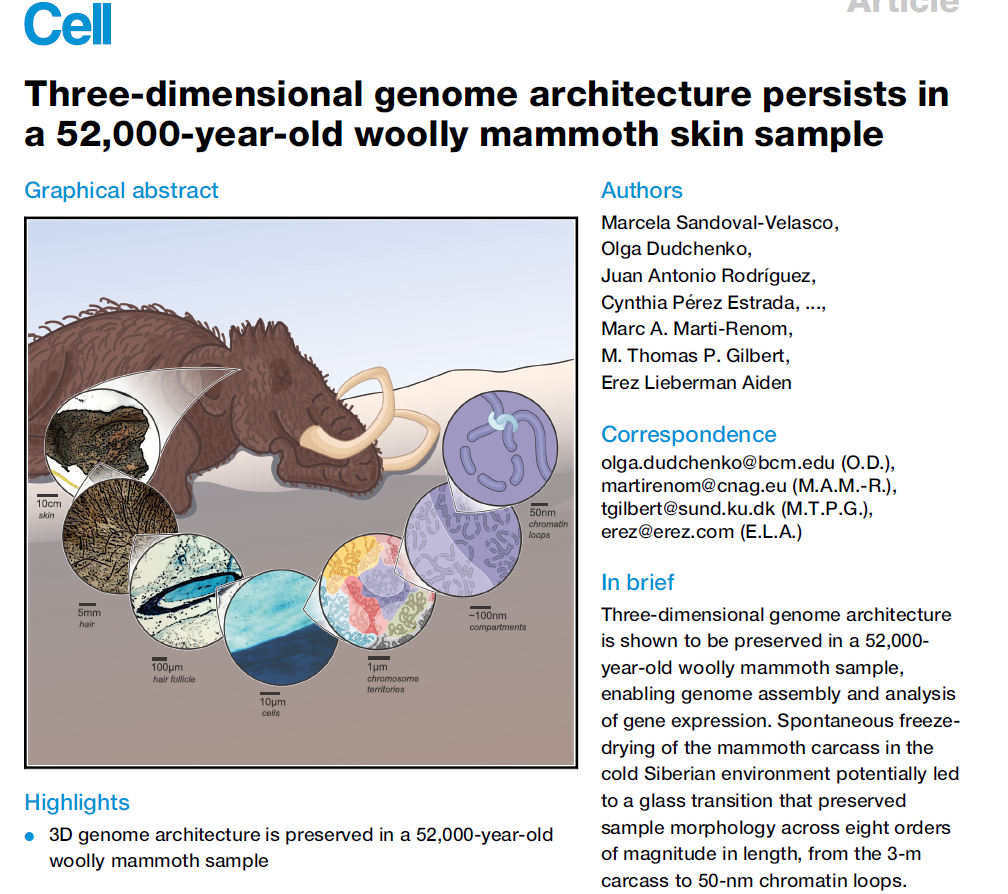
Graphical abstract
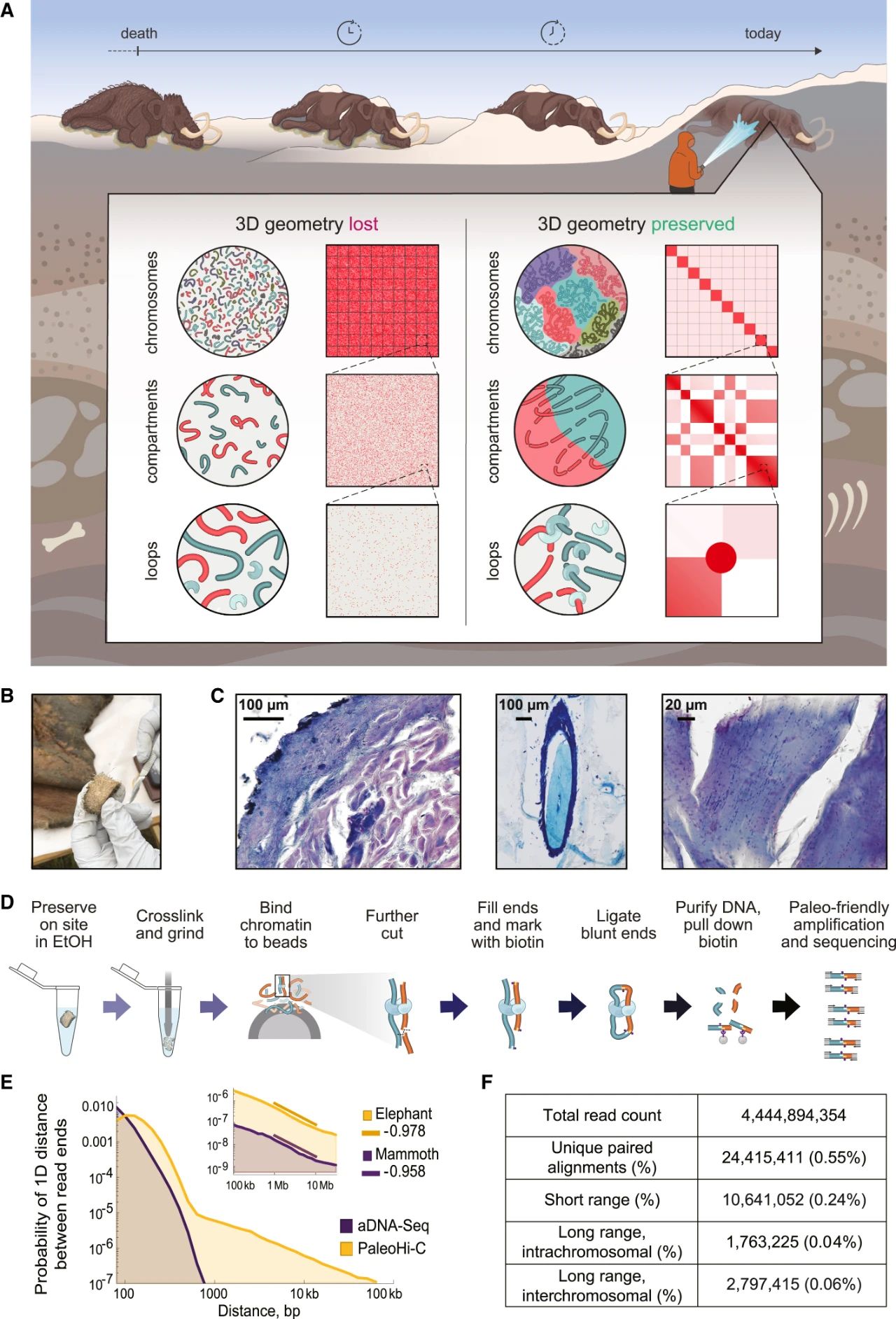
Figure 1 | PaleoHi-C reveals that the morphology of chromosomes is preserved in a 52,000-year-old sample of woolly mammoth skin
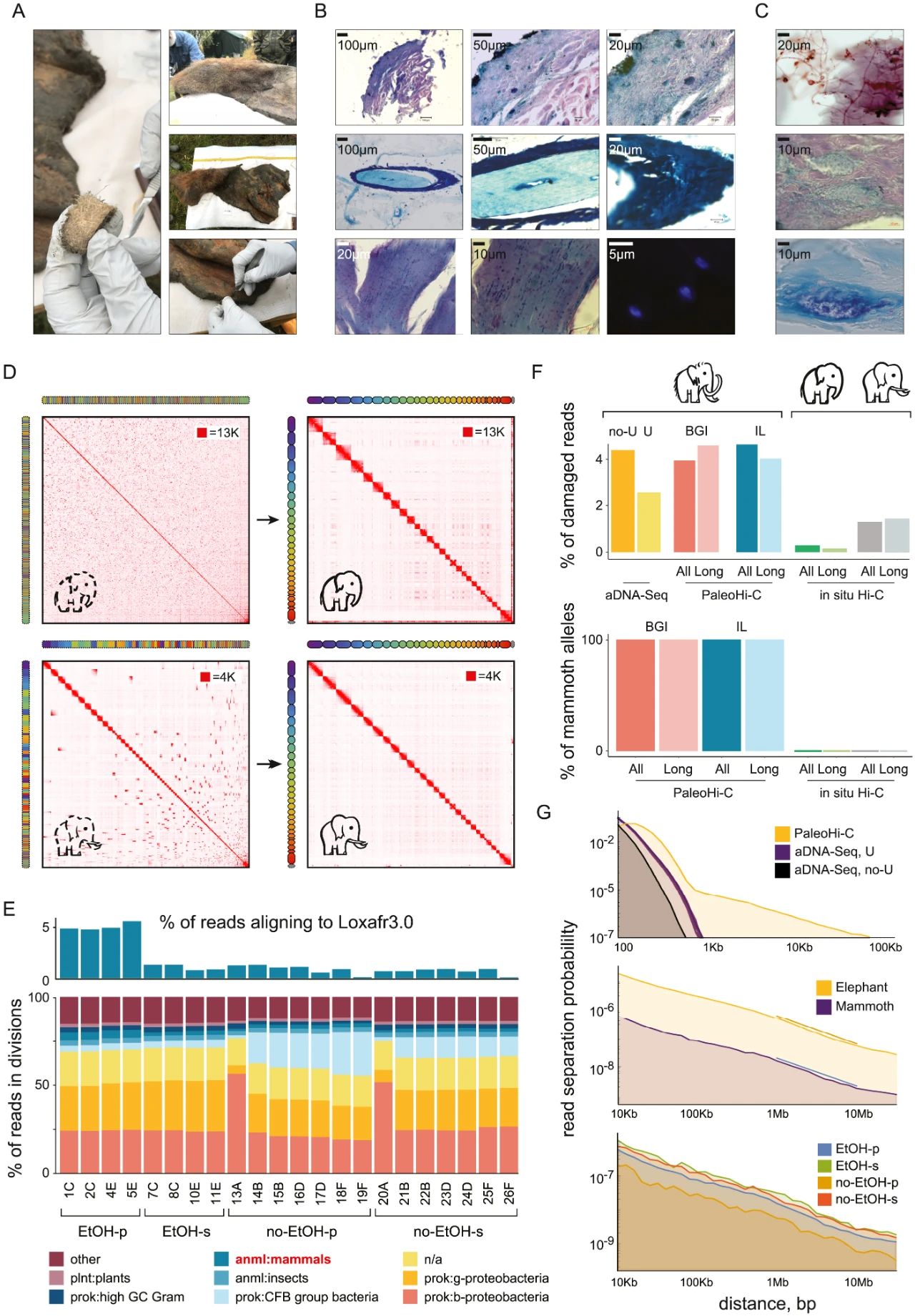
Figure S1 | PaleoHi-C read pairs aligning to elephant derive from authentic ancient mammoth DNA and reflect the ancient chromosome conformation
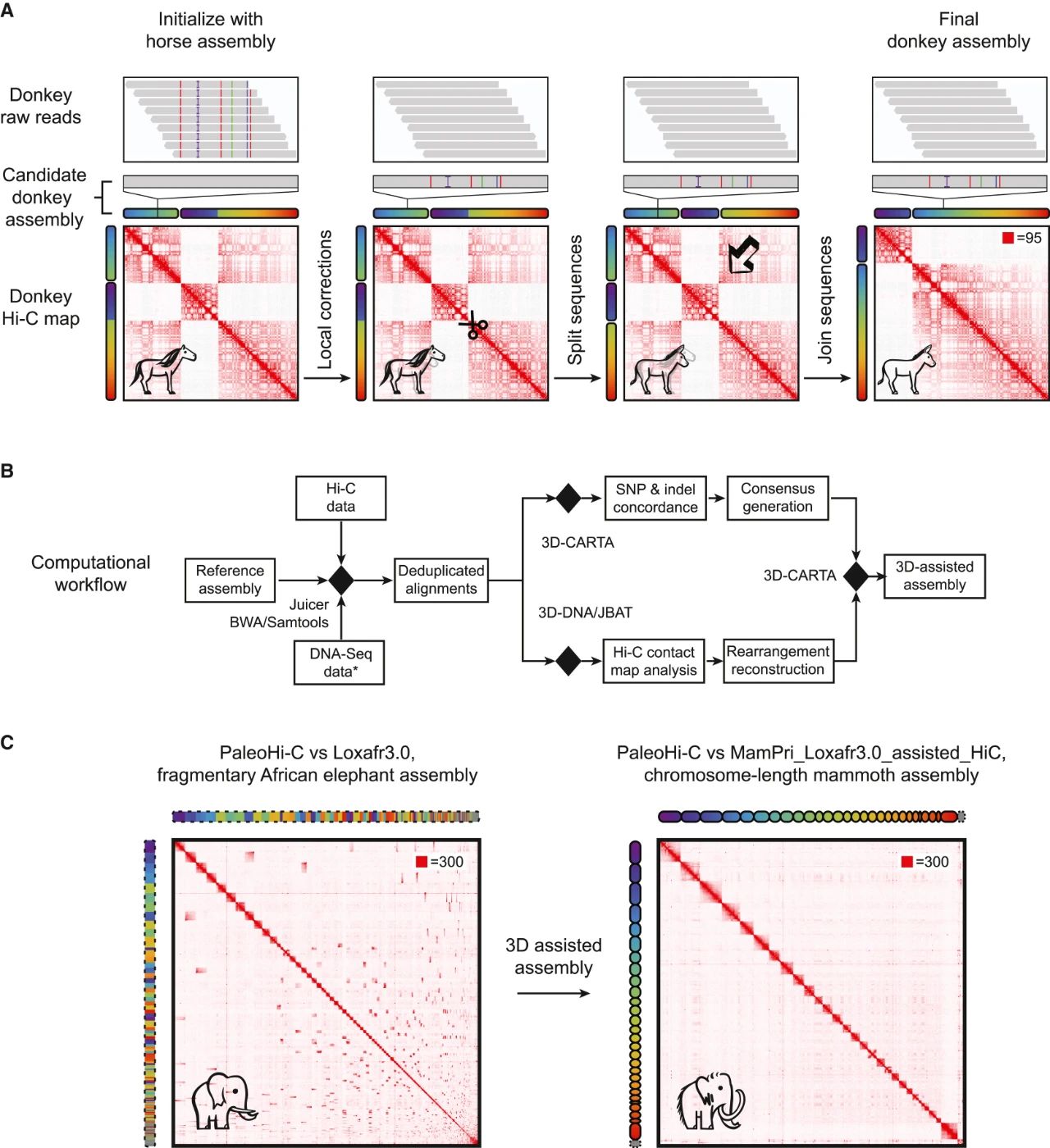
Figure 2 | We developed reference-assisted 3D genome assembly and used it to assemble a woolly mammoth genome with chromosome-length scaffolds
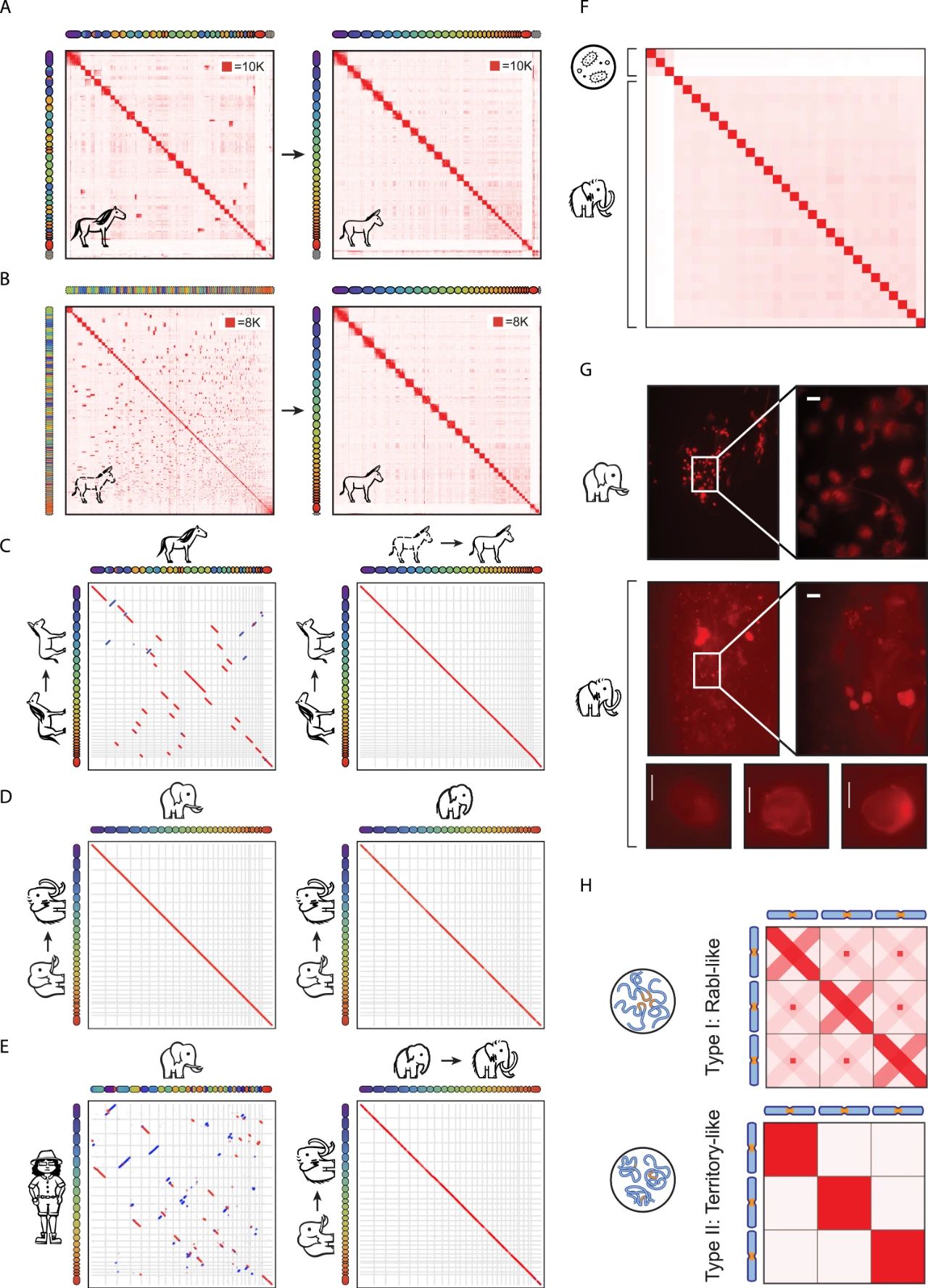
Figure S2 | Reference-assisted 3D genome assembly of a woolly mammoth yields a robust karyotype consistent with modern elephantids

Figure 3 | Segregation between active (A) and inactive (B) genome compartments can survive in ancient samples, enabling comparison of gene activity in woolly mammoth and Asian elephant skin
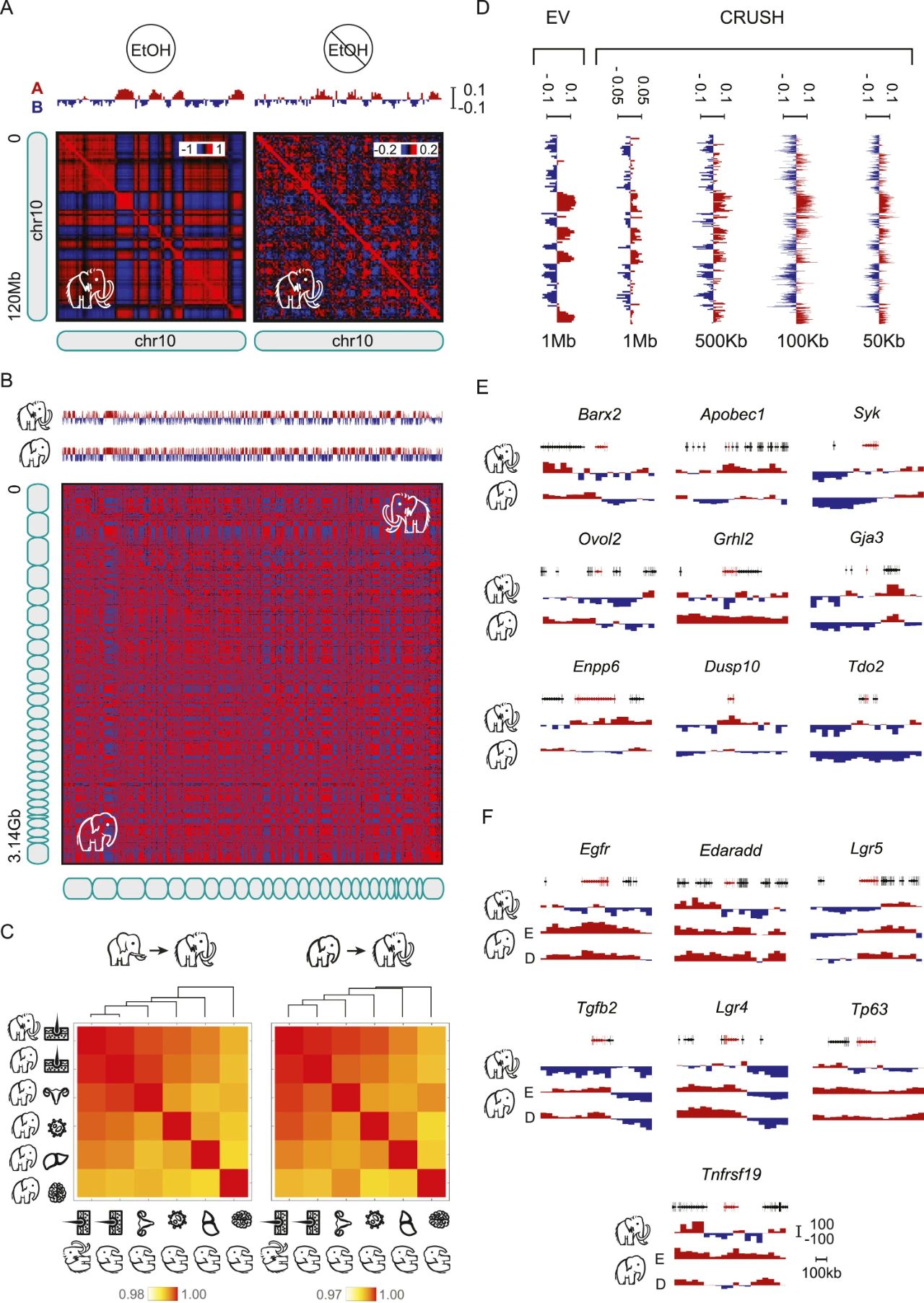
Figure S3 | The segregation of active (A) and inactive (B) chromatin in the woolly mammoth sample preserves the cell-type specific compartmentalization of ancient woolly mammoth chromosomes
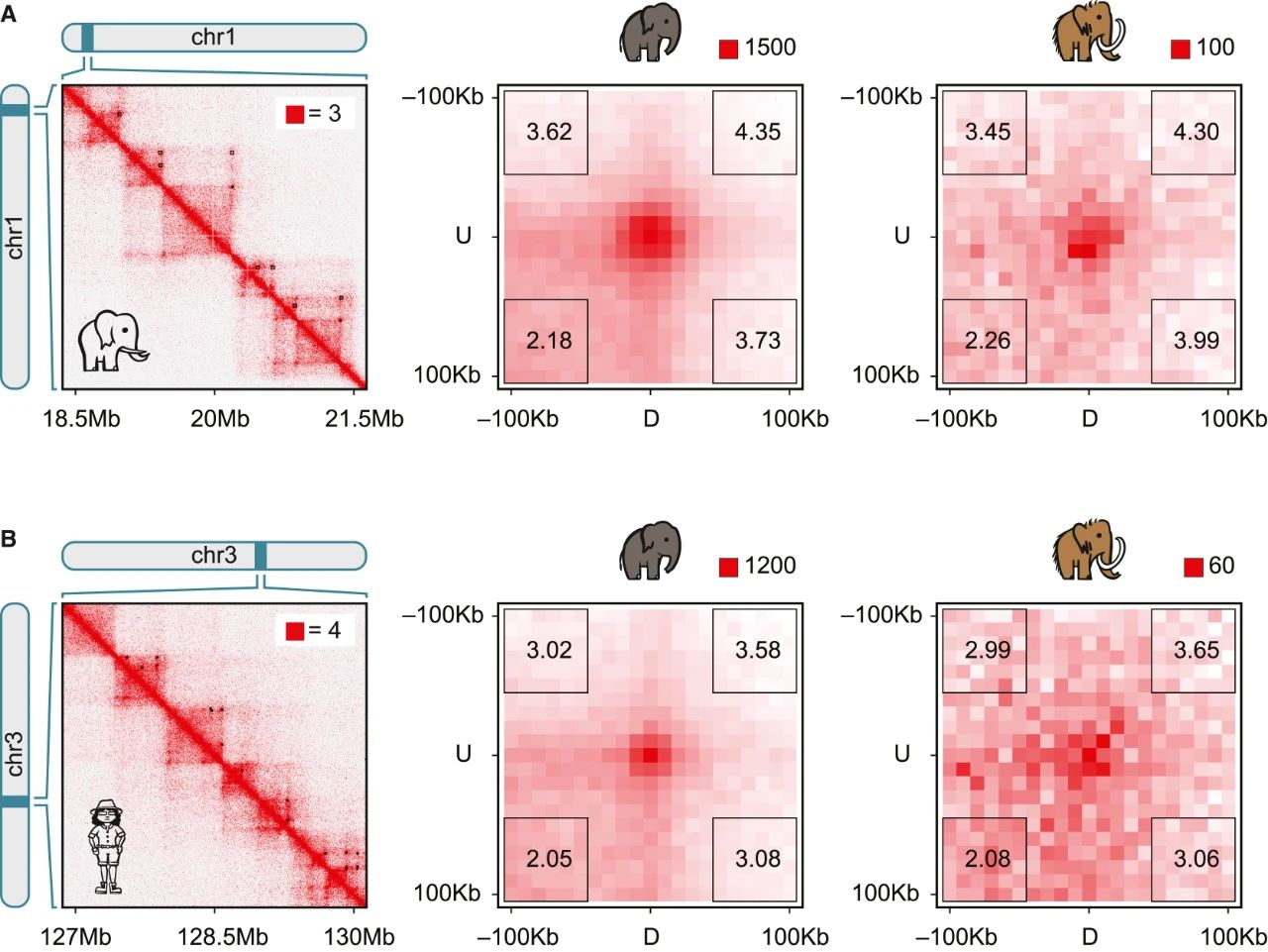
Figure 4 | Chromatin loops can survive after 52,000 years in permafrost
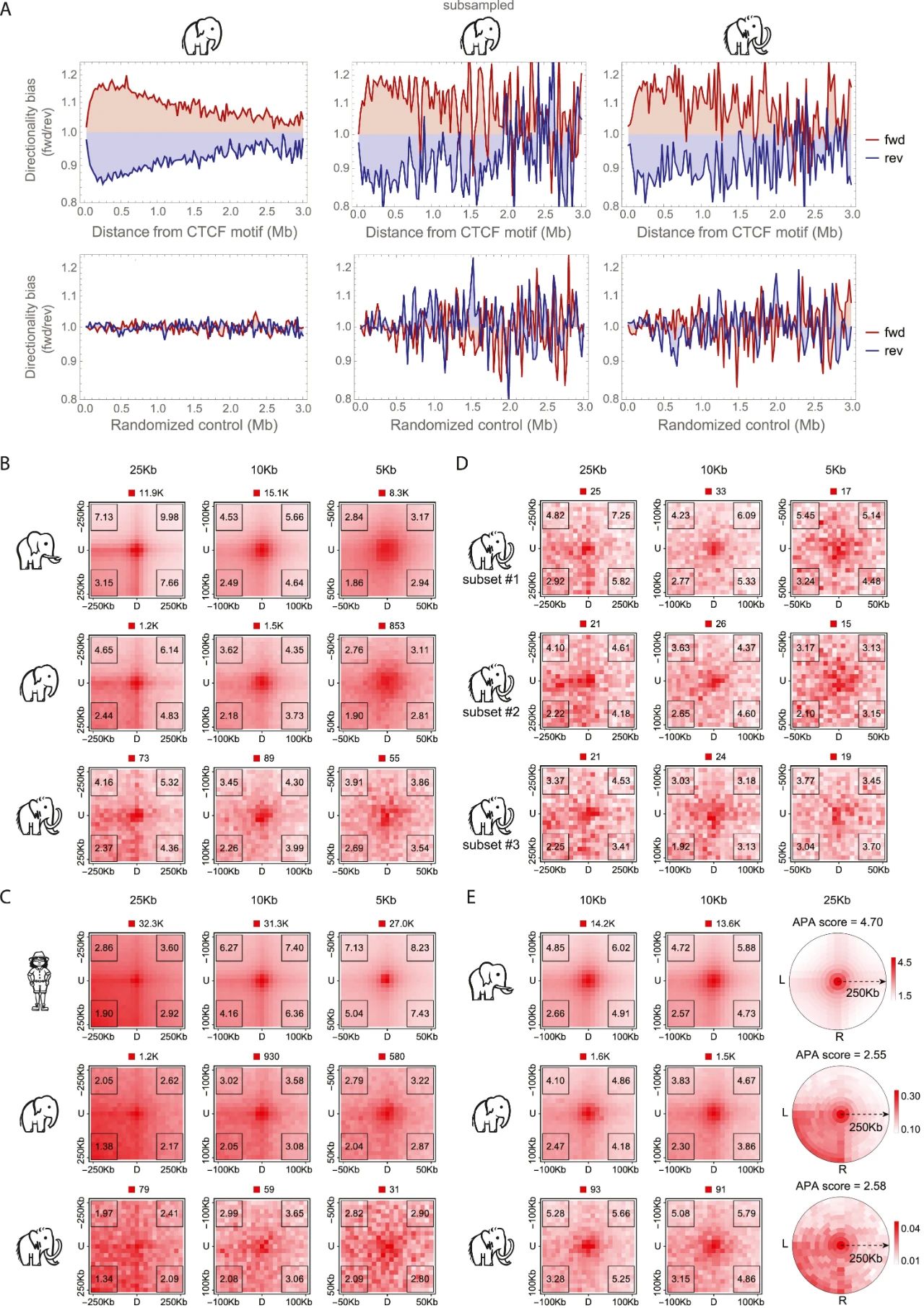
Figure S4 | Remains of point-to-point looping and ancient loop extrusion persist in woolly mammoth skin
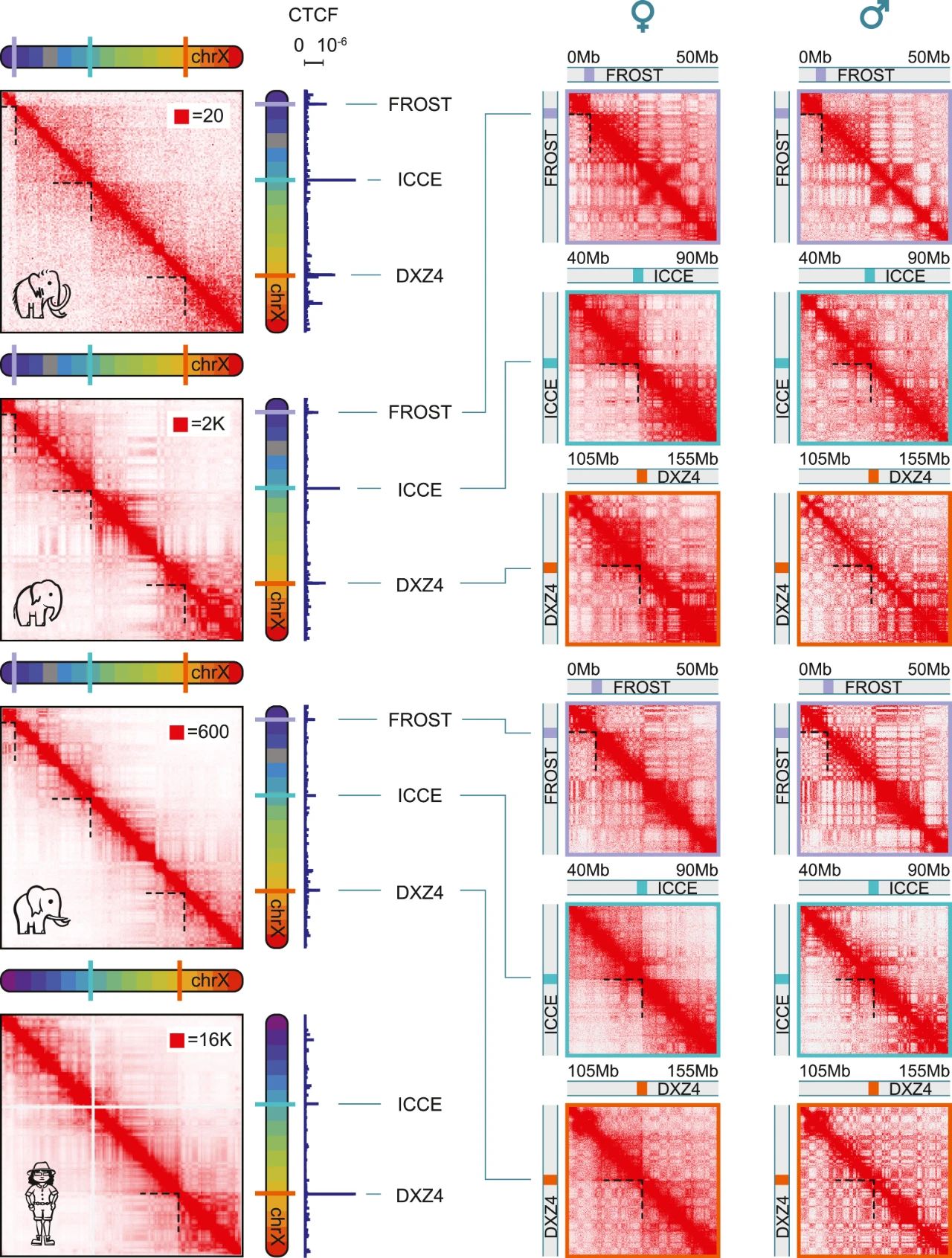
Figure 5 | The inactive X chromosome (Xi) in woolly mammoths exhibits a tetradic structure, with 4 superdomains, distinct from the bipartite structure in humans
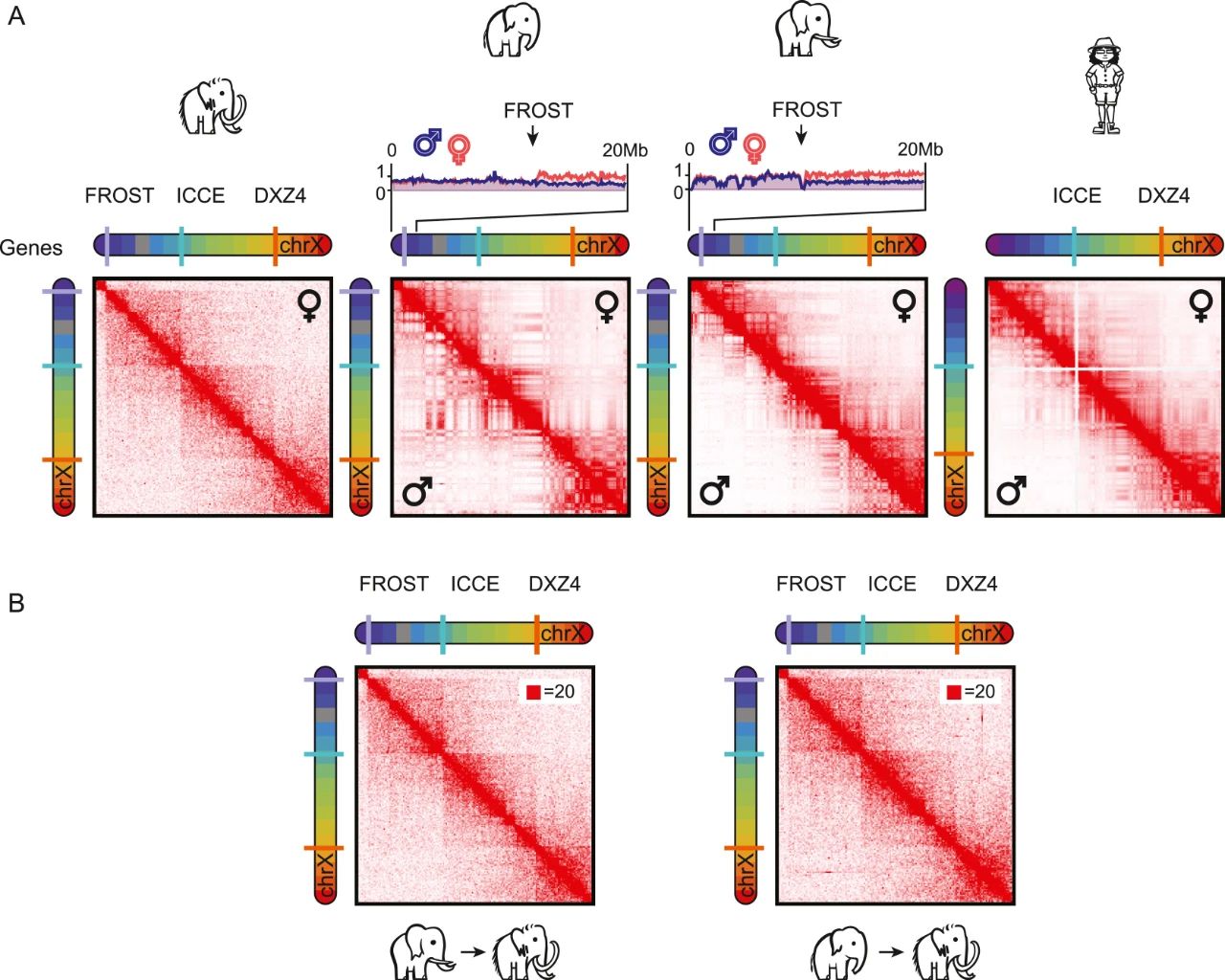
Figure S5 | The FROST superdomain boundary element flanks the elephantid pseudoautosomal region (PAR)
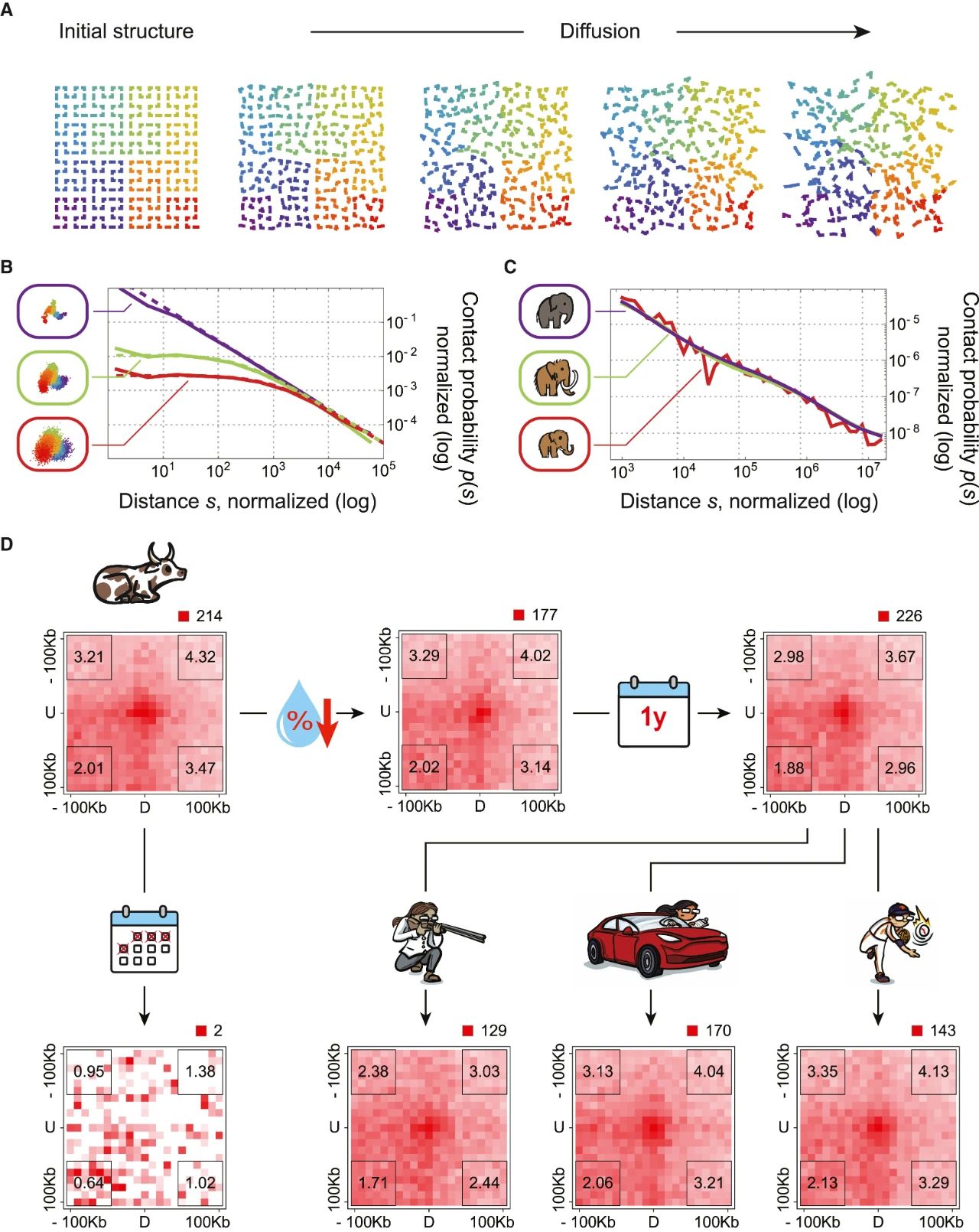
Figure 6 | The mammoth DNA in our sample has diffused minimally, in line with the resilience of chromatin architecture in modern dehydrated samples
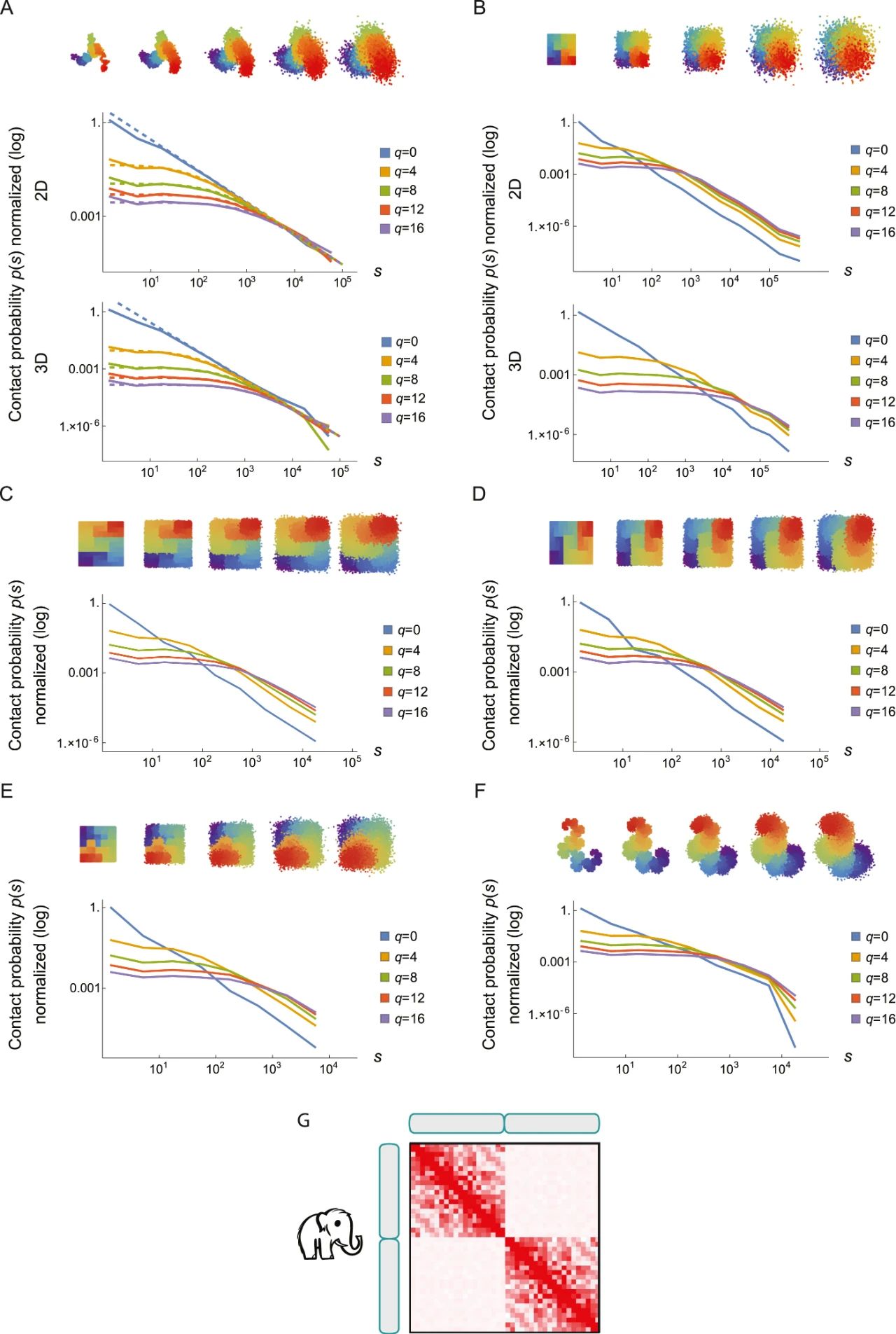
Figure S6 | Nuclear architecture is preserved in Yuka, a juvenile female woolly mammoth from 39,000 years ago
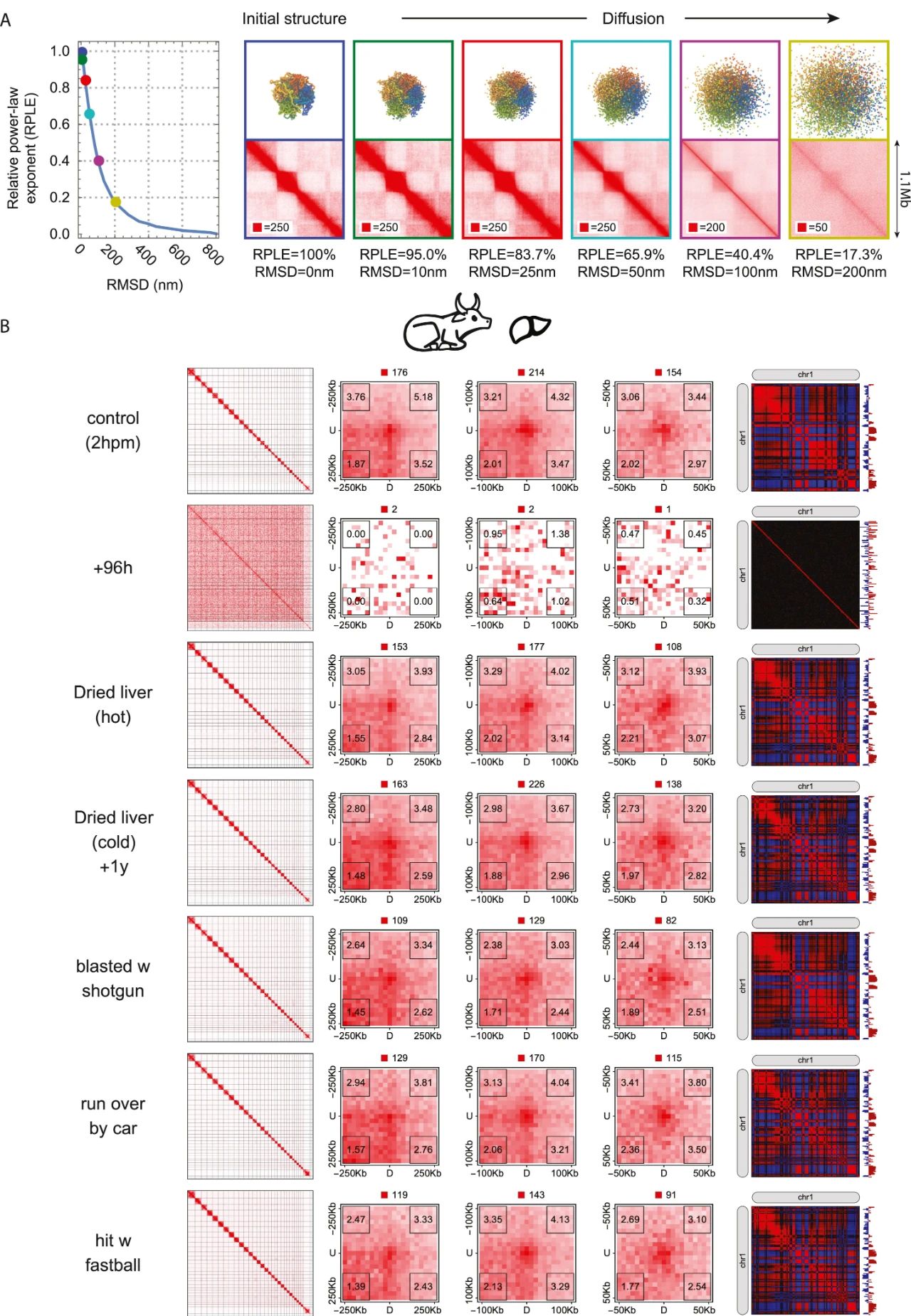
Figure S7 | In dehydrated tissue samples exposed to room temperature, nuclear architecture is preserved for a year

Figure 7 | We hypothesize that the woolly mammoth samples studied here contain chromoglass—chromatin trapped in a glassy state, where molecular diffusion is minimal
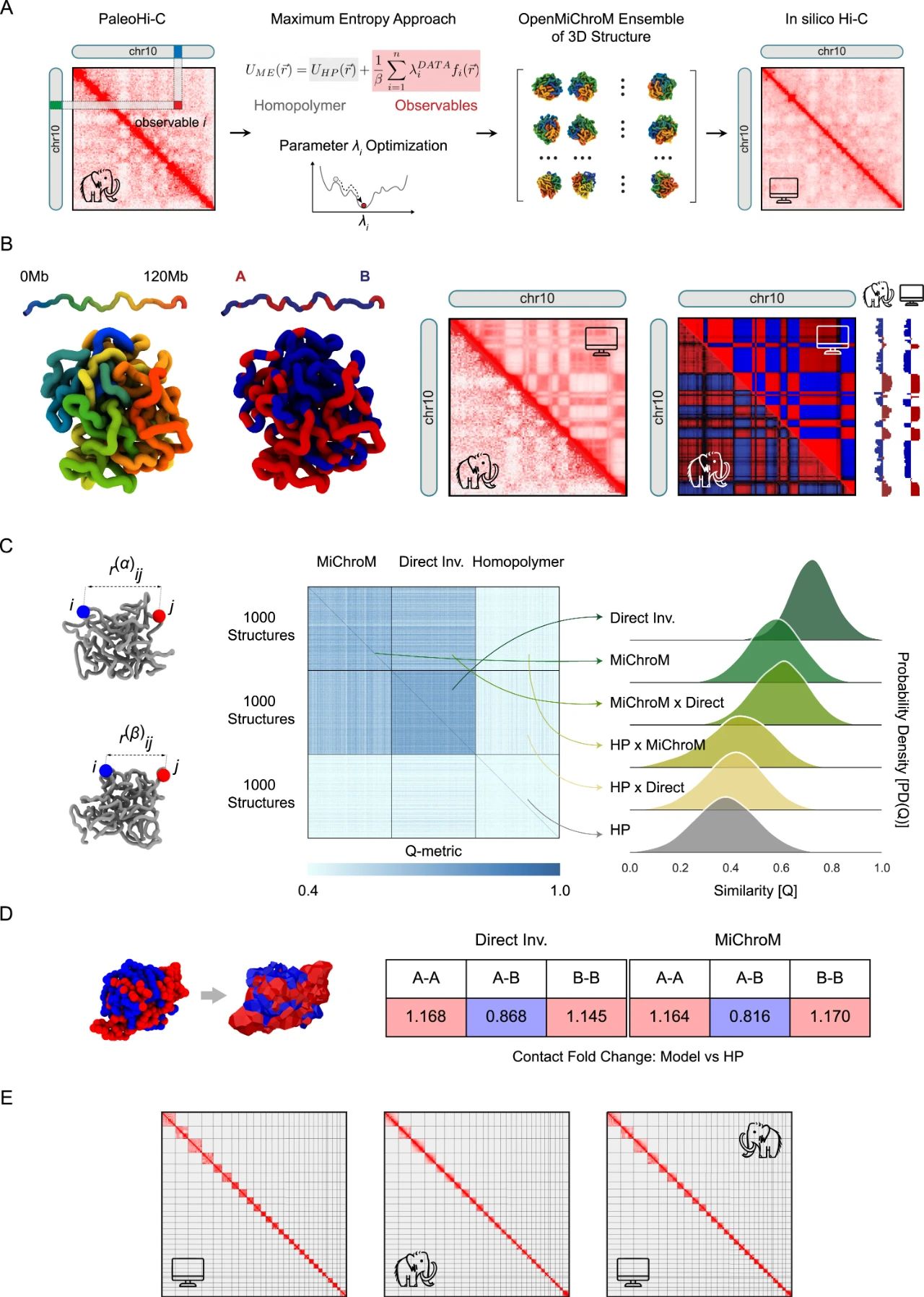
Figure S8 | The 3D structural ensemble inferred from PaleoHi-C data is robust to the choice of modeling strategy
转载来源:MEPGT公众号
原文链接:https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0092867424006421?via%3Dihub=