北戴河地区鸻形目鸟类觅食生境动态变化研究
发布时间:2009年05月11日 作者:倪永明
倪永明1,2 李湘涛1
(1 北京自然博物馆,100050 2 中国科学院生态环境研究中心 10085)
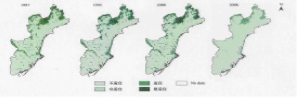
摘要:生境破坏是目前野生动物保护面临主要问题,加强生境恢复与重建对保护珍稀物种具有重要意义。本文将3S技术运用到北戴河地区鸻形目鸟类觅食生境评价中,分析了近20年(1987-2006)北戴河地区鸻形目鸟类觅食生境的动态变化,具体结果如下:鸻形目鸟类最适宜觅食生境和适宜觅食生境分布面积在1993年最大;觅食生境变化以1993年为分水岭;最适宜觅食生境和适宜生分布面积呈下降趋势(倒U形分布),不适宜觅食生境分布面积呈增加趋势(U形分布)。北戴河地区鸻形目鸟类觅食生境变化主要影响因素是人类活动增加。
关键词:北戴河;鸻形目鸟类;觅食生境适宜性评价
Suitability Evaluation of Plover Birds’ Foraging Habitat in Beidaihe Areas Based on GISNi yongming1, 2 Li xiangtao1
(1 Beijing Museum of Nature History, 100050; 2 Research Center of Eco-Environmental Sciences, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 100085)
Abstract: Habitat losses and fragmentation is one of the most serious ecological crises that threaten the wildlife all the world. Therefore, it is very important to strengthen the ecological restoration to conserver these endangered species. In the study, we applied 3S techniques to evaluate the change of Plover Birds’ Foraging Habitat near Bei Dai he region during the past two decades (1997-2006). It showed the range of the birds’ foraging habitats kept increasing until 1993 which was the tuning point. Then, after 1993 the range of birds’ foraging habitats kept decreasing. Thus, the curve of the distribution of the most suitable foraging area is inverted u-shaped. In contrast, the curve of the distribution of the unsuitable foraging area is u-shaped. The dense human activities are the main reasons resulted in the significant change of the birds’ foraging habitats.
Keywords: Bei dai he, Plover Birds, Suitability evaluation of foraging Habitat.



 京公网安备11010102006642号
京公网安备11010102006642号