一些攀禽跗跖骨远端形态结构与对趾足之间的关系分析
发布时间:2009年07月29日 作者:张玉光
张玉光
摘 要 鹦形目、鴷形目、鹃形目等攀禽的趾型是对趾足类型,这种趾型与该鸟类的跗跖骨形态结构表现出极度的适应性。特别是第Ⅳ跖骨滑车发生的显著翻转以及膨大的副关节突的出现,使鸟类在实现和完成对趾足的功能时显得更加完善。这些作为攀禽中部分对趾足的鸟类,为适应多样的生活习性而在跖骨结构上发生的变化是特化的表现,也是相互协同的结果。
关键词 攀禽 跗跖骨远端 第Ⅳ跖骨滑车 对趾足 适应
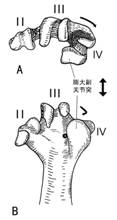
牡丹鹦鹉左跗跖骨远端的形态特点
(Left tarsometatarsus characters)
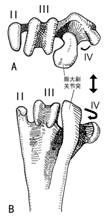
大斑啄木鸟左跗跖骨远端的形态特点
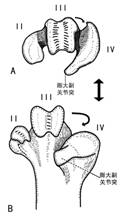
大杜鹃左跗跖骨远端的形态特点
( A:末端视 B:远端后视)
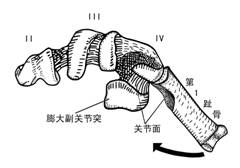
对趾足鸟类第Ⅳ跖骨滑车与其第1趾骨的连接方式(以鹦鹉为例)
The fourth trochlea and its conjunction with the first Phalange of Agapornis fischeri
Morphology of Distal End Tarsometatarsus and Zygodactylousin Some Scansores
ZHANG Yu-Guang
Abstract The foot character of Scansores such as Psittaciformes,Piciformes and Cuculiformes was the zygodactyl foot,of which the shape and structure and that of avian tarsometatarsus presented the exceeding adaptability. In particular, the permanently reversed metatarsal trochlea Ⅳ and enlarged accessory articulating process made the function of avian zygodactyl foot perfect. The structural change of metatarsus of these zygodactyl birds, as a member of Scansores,in order to adapt to the various life habits was a kind of specialization behavior,and a kind of coordination.
Key words Scansores, Distal end tarsometatarsus, Metatarsal trochlea Ⅳ, Zygodactyl foot, Adaptation
《动物学杂志》,2007,42(3):126-130



 京公网安备11010102006642号
京公网安备11010102006642号